Explain How Different Temps Affect Enzymes Proteins
List the factors that can affect the rate of a chemical reaction and enzyme activity. Although higher temperatures increase enzyme activity and reaction rate enzymes are still proteins and like all proteins temperatures above 40 degrees Celsius will begin to break their activity.
Factors Affecting Enzyme Action
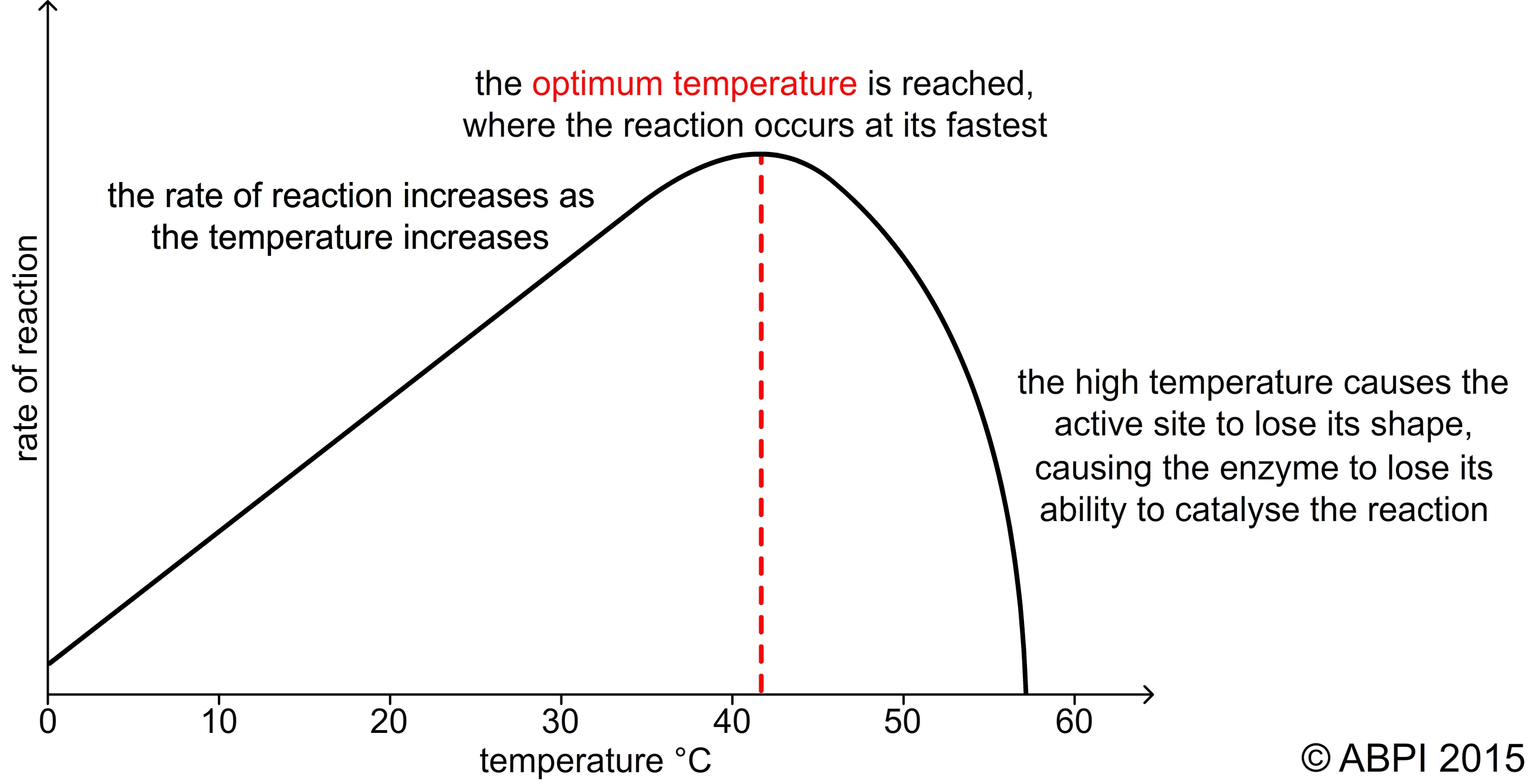
Although increased temperatures can cause enzymes to work more quickly if the temperature gets too high the enzyme stops working.
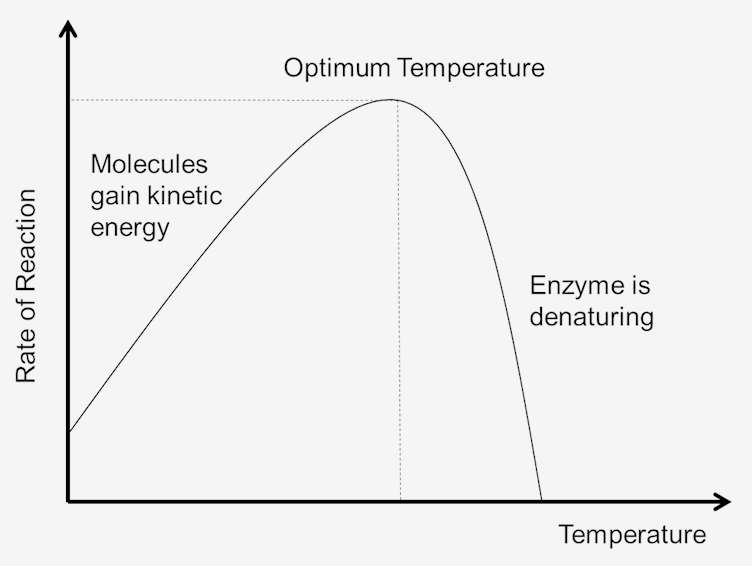
. Increasing the temperature of an enzyme catalysing reaction will increase the kinetic energy of the molecules and therefore the rate of reaction. In this lab you will study an enzyme that is found. Explain the effect of increased enzyme concentration on an enzyme-catalysed reaction.
Enzyme activity occurs within a narrow range of temperatures compared to ordinary chemical reactions. You have hundreds of different enzymes in each of your cells. If the temperature is increased the molecules will gain kinetic energy allowing them to move a lot more frequently.
Enzymes are proteins that act upon substrate molecules and decrease the activation energy necessary for a chemical reaction to occur by stabilizing the transition state. The temperature at which the enzyme activity is greatest. Its important to note that different enzymes have different ideal temperature and pH.
Temperature affects enzymes by increasing the bond energy causing the atoms in the enzymes bonds to drift apart from each other. A minimal increase in temperature causes an increase in the enzyme activity rate. A ten degree centigrade rise in temperature will increase the activity of most enzymes by 50 to 100.
Variations in reaction temperature as small as 1 or 2 degrees may introduce changes of 10 to 20 in the results. At this point the addition of more enzymes wont increase rate of reaction. An enzyme activity is maximum within a narrow range of temperature.
- it increases until no. This stabilization speeds up reaction rates and makes them happen at. Factors that affect rate of enzymes.
The effect of temperature on enzyme activity has been described by two well-established thermal parameters. The shape of an enzyme also depends on its temperature. This is due to the fact that molecules move faster in heat than cold.
Enzymes are protein machines that have a special three-dimensional shape just as different sized bird beaks are good at eating different types of fruits and insects. The amino acids in biological systems have substituents known as carboxyl functional groups and. The protein nature of the enzymes makes them extremely sensitive to thermal changes.
The effect of Temperature on Enzyme The rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction is affected by changes in temperature Each enzyme has a temperature that it works optimally in called Optimum Temperature For most enzymes the optimum temperature is at or above the temperature of the cells in which the enzyme is found in vivo. The Arrhenius activation energy which describes the effect of temperature on the catalytic rate constant k cat and thermal stability which describes the effect of temperature on the thermal inactivation rate constant k inact. Explain why enzymes have an optimal pH and temperature to ensure greatest activity greatest functioning of the enzyme be sure to consider how virtually all enzymes are proteins and the impact that temperature and pH may have on protein function.
When they are just the right temperature then they are just the right shape and the chemical reactions that they catalyze take place at the optimal rate and with the most ease. If the temperature around an enzyme gets too high the enzyme loses its shape which is known as denaturation and ceases to work. However as the temperature exceeds the optimum the rate of reaction will decrease.
Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity. Enzyme Function Dependent On Temperature. Enzyme molecules is greater than the no.
Therefore the two ends of the enzyme activity range depend on what temperature the temperature starts to act on and what temperature begins to decompose the protein. As the temperature increases so will the rate of enzyme reaction. The temperature at which an enzyme shows its maximum activity is called optimum temperature.
I predict that at temperatures above 70C the enzyme lipase will become denatured and at temperatures below 10C the enzyme will become inactive. Generally an increase in temperature tends to increase the movement of molecules in a system. Because so much of an enzymes activity is based on its shape temperature changes can mess up the process and the enzyme wont work.
- rate of reaction increases. At very low temperatures the molecule becomes rigid and cannot undergo the necessary conformational. Most enzymes will become denatured at very high temperatures.
However when the temperature becomes too high the enzymes will have too. Up to 24 cash back Enzymes are proteins that speed up the rate of reactions that would otherwise happen more slowly. Optimum Temperatures Every enzyme has an optimum temperature.
Each of these enzymes is responsible for one particular reaction that occurs in the cell. Active sites of enzymes bring substrate molecules closer together and thus increase the chance that the molecules will interact. Enzymes begin a reaction when they randomly collide with the substrate molecule this is where the enzyme will react upon.
And when they get too cold then they get too tight. The enzyme is not altered by the reaction. The activity of enzymes can be affected by temperature and pH.
Therefore as the temperature is increased the enzyme activity and the rate of reaction increases. Each enzyme has an optimal temperature range meaning the enzyme has highest activity somewhere near the middle of that range. This can be different from one enzyme to the next but enzymes within the human body tend to have optimum temperatures around 37C.
The following two models have been proposed to explain the formation of the E-S complex. The speed and frequency of these collisions is dependent on the temperature so an increase in. Look at the graph to the right as the temperature increases so does the enzymes activity.
At high temperatures the weak hydrogen bonds holding the enzyme in a 3-D shape start to break and the enzyme denatures. As you have seen each enzyme has a certain temperature at which it is more active. Every day trillions upon trillions of chemical reactions occur in our body to make essential metabolic processes occur.
When enzymes get too warm they get too loose. Proteins change shape denature as temperatures change. The factors affecting enzyme activity are.
As temperature increases so do the rate of enzyme reactions. Effect of Temperature on Enzymatic Reaction.

Effect Of Temperature On Enzymatic Reaction Creative Enzymes

Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity A Level Biology Revision Notes
Comments
Post a Comment